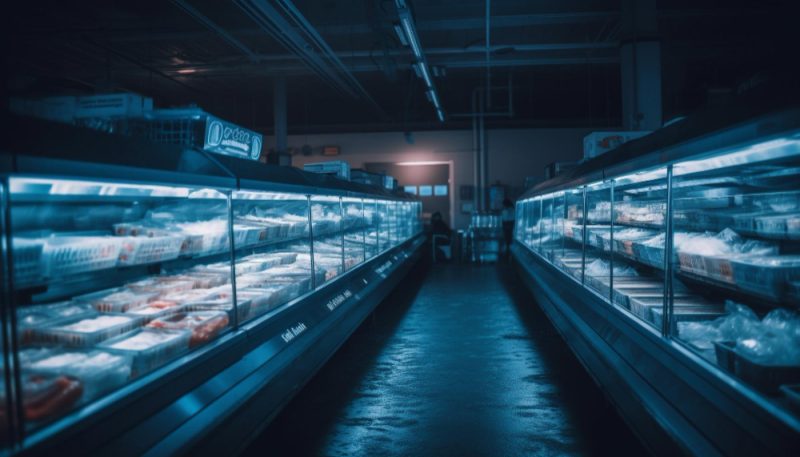
Cold chain logistics play a critical role in industries where temperature control isn’t optional. Food, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and specialty chemicals all depend on precise handling to preserve safety, quality, and compliance. When cold chain operations fail, the consequences can be costly — or even dangerous.
Not all cold chain partners are created equal. While many providers claim to offer temperature-controlled services, the best ones distinguish themselves through consistency, transparency, and operational discipline. Knowing what sets top-tier cold chain partners apart can help businesses protect their products and their reputations.
Relentless Focus on Temperature Integrity
The defining characteristic of a strong cold chain partner is an uncompromising commitment to temperature control. This goes beyond having refrigerated storage or climate-controlled trucks. It involves maintaining strict temperature ranges across every stage of handling, storage, and transportation.
Top providers design processes around temperature integrity, not convenience. They minimize door openings, reduce dwell time, and plan workflows to prevent exposure during transfers. Equipment is calibrated regularly, and temperature tolerances are treated as non-negotiable standards rather than flexible guidelines. Consistency matters more than promises, and the best partners build systems that perform reliably under real-world conditions.
Robust Monitoring and Real-Time Visibility
Leading cold chain partners invest heavily in monitoring technology. Continuous temperature tracking, automated alerts, and data logging are standard these days, not optional. Real-time visibility allows issues to be identified and addressed before they escalate. If temperatures drift out of range, corrective action can happen immediately rather than after product integrity is already compromised.
Equally important is access to data. Strong partners provide clear, accessible temperature records that support audits, quality assurance, and regulatory compliance. Transparency builds trust and reduces uncertainty throughout the supply chain.
Strong Quality Control and Documentation Practices
Cold chain operations require meticulous documentation. From receiving and storage logs to shipment records and deviation reports, paperwork is a critical part of protecting product integrity. The best partners treat documentation as an operational priority rather than an administrative burden. Processes are standardized, records are complete, and deviations are investigated rather than ignored; and this attention to detail is especially important in regulated industries, where incomplete documentation can be just as damaging as a temperature excursion itself.
Proactive Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Cold chain failures often occur during unexpected events: equipment breakdowns, power outages, weather disruptions, or transportation delays. The best cold chain partners plan for these scenarios in advance. Contingency plans may include backup power systems, redundant refrigeration units, alternative transportation routes, and predefined escalation procedures. Staff are trained to respond quickly and decisively when conditions change. Rather than reacting to problems after the fact, top providers anticipate risk and build resilience into their operations.
Trained Staff With Cold Chain Expertise
Technology alone doesn’t ensure cold chain reliability. People matter just as much. The best partners invest in training employees who understand the importance of temperature control and the consequences of mistakes.
From warehouse staff to drivers and supervisors, everyone involved in handling temperature-sensitive products should be trained in proper procedures, hygiene standards, and emergency response. Experience also plays a role; teams that regularly handle cold chain products are better equipped to spot subtle warning signs and prevent issues before they escalate.
Facility Design That Supports Cold Chain Flow
Physical infrastructure is another differentiator. Leading cold chain partners design facilities specifically for temperature-sensitive operations rather than retrofitting general warehouses. Features such as temperature-zoned storage, rapid-access cold rooms, insulated loading docks, and controlled transfer areas help maintain product integrity during movement. And efficient layouts reduce handling time and limit exposure.
Regulatory Knowledge and Compliance Readiness
Cold chain logistics often operate under strict regulatory frameworks, and the best partners stay current with relevant standards and understand how those requirements apply to daily operations. Compliance isn’t treated as a checkbox exercise here. Instead, it’s integrated into training, documentation, and process design. Partners who understand regulatory expectations are better prepared for audits and less likely to expose clients to compliance risk.
Clear Communication and Accountability
Cold chain operations require constant coordination. Delays, changes, or issues must be communicated quickly and clearly to prevent downstream problems, so the strongest partners establish clear points of contact, provide timely updates, and communicate proactively rather than defensively. When issues occur, accountability matters more than excuses. Clients benefit from partners who explain what happened, how it was addressed, and what steps will prevent recurrence.
Why the Best Cold Chain Partners Earn Trust Over Time
Cold chain partnerships are built on reliability. One successful shipment isn’t enough: their performance must be repeatable, measurable, and consistent. The best cold chain partners stand out because they combine technology, training, infrastructure, and discipline into a cohesive operation. Ultimately, they reduce uncertainty, protect product integrity, and support long-term business relationships.